
When lane keeping aid is enabled, the vehicle can alert you if you are about to drift out of your lane. It can also perform steering interventions. The lane keeping aid depends on the vehicle's forward-facing camera to identify road markings and your position in the lane.
Warning
Main conditions for lane keeping aid
- Your speed must be in the 60-180 km/h range (40-110 mph).
- The lane markings must be clearly visible for the vehicle's camera to see.
- The lane must be wide enough. A very narrow lane does not provide enough margin between the vehicle and the road markings.
- You must keep your hands on the steering wheel and actively steer the vehicle.
Important
Steering actively
Never let go of the steering wheel when driving. Do not dismiss the vehicle's requests for you to steer actively and keep your attention on the road.
Lane keeping aid intervention types
| Steering intervention | The vehicle tries to steer back into the lane. |
| Lane departure warning | The vehicle alerts you using sound and steering wheel vibrations. |
Note
Signaling a turn or lane change
As long as you use the turn signals when changing lanes, the vehicle assumes that you are making an intentional maneuver.
Cutting a corner
The lane keeping aid may allow you to briefly cut across the lane marker while navigating a sharp corner.
Safety interventions are always enabled
Some situations can cause a steering intervention to prevent a dangerous lane departure even if lane keeping aid is turned off in settings.
Display symbols and communication
Lane keeping aid warnings and interventions are communicated in the instrument panel.
 | This symbol appears if you are coming too close to the lane markings. The symbol is mirrored during left-side warnings. |
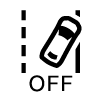 | This symbol indicates that lane keeping aid is disabled in settings or temporarily unavailable. |
 | This symbol appears when there is a lane keeping aid malfunction. This means that lane keeping aid and safety interventions to prevent lane departures are disabled. |
Conditions and limitations
For lane keeping aid to work, road markings must be present and visible. The vehicle identifies them using a forward-facing camera. This form of detection requires the camera view to be unobstructed and the conditions for visual detection to be present. Read the separate section about the conditions and limitations of your vehicle's cameras to understand how features relying on camera detection are affected.
- Lane splits and merges can cause temporary misidentification of the lane.
- Non-standard or unusual road marking layouts might not be identified correctly by the vehicle. For example, road work or traffic diversions can result in conflicting or multiple sets of road markings.
- The vehicle may be unable to detect deteriorated road markings: for example, if they are worn, misshapen or discolored.
- Other edges or lines can be misidentified as road markings, such as curbs, road surface repair edges, barriers or well-defined shadows.
- Road markings must be sufficiently illuminated to be detected. In low-light conditions, they need to be illuminated by the vehicle or street lights.